Ischemia: Causes, Challenges, and a Proposed Device for Treatment (Oxygen-Compressed Centrifuge for Physiotherapy)
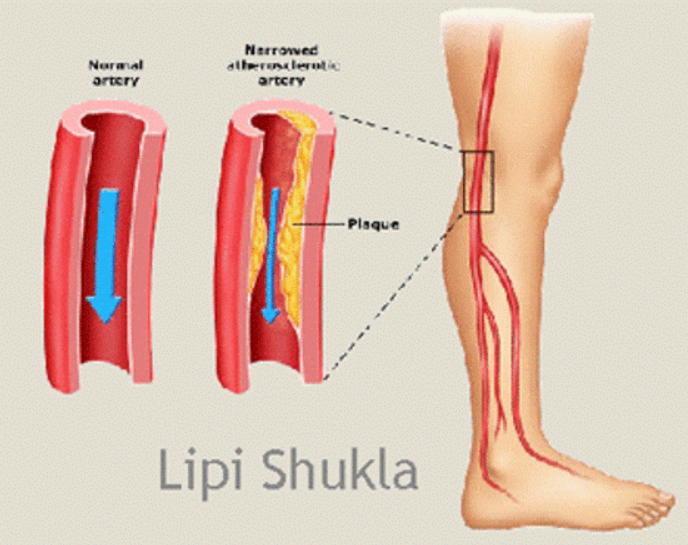
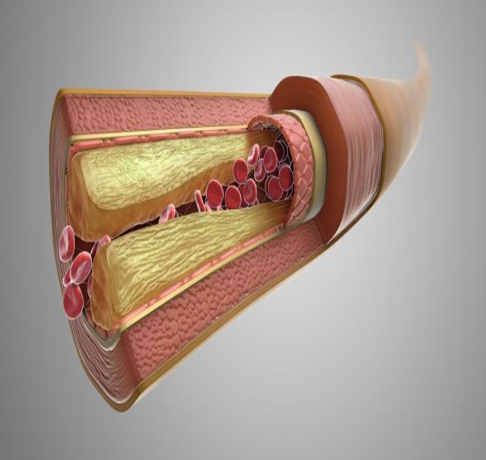
Ischemia, commonly referred to as a lack of blood supply due to narrowing or blockage of blood vessels, is a growing global health concern. The disease is associated with multiple risk factors such as diabetes, hypertension, high blood cholesterol, and smoking. Current treatments rely mainly on drugs and surgical interventions, which are often temporary and insufficient for treating microvascular complications. This research introduces a patented medical device—an oxygen-compressed centrifuge through physiotherapy—designed to treat ischemia non-invasively, with reduced risks and environmental impact.
Introduction
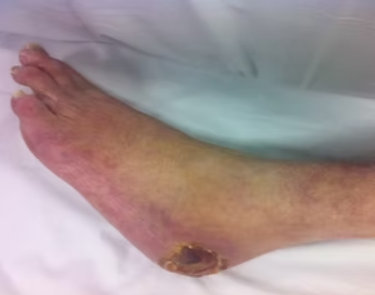
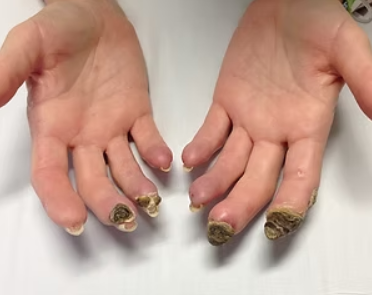
Ischemia, or the narrowing and blockage of blood vessels, has become increasingly identifiable due to advances in modern diagnostic imaging. Although early detection has improved, treatment continues to depend largely on medicinal compounds and surgery. Surgical intervention, while sometimes necessary, is often a temporary solution and may result in complications such as limb amputation, particularly in advanced cases that develop gangrene due to peripheral vascular occlusion.
The rise in ischemia cases is strongly linked to lifestyle and health-related factors, including smoking, elevated cholesterol levels, diabetes, and hypertension. As the global prevalence increases, the demand for safer, more effective, and environmentally friendly treatment alternatives grows.
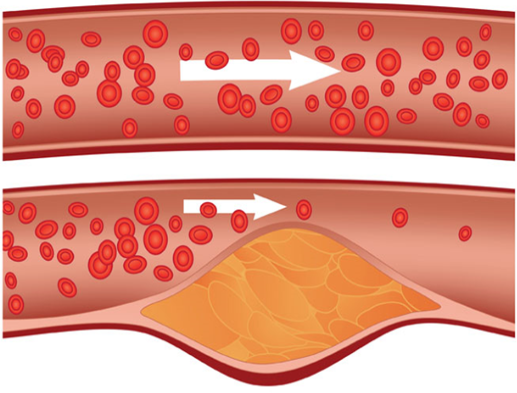
Current Treatment Limitations
Standard ischemia treatments involve:
- Medication: Chemical compounds that manage symptoms but cannot address tiny blocked vessels.
- Surgery: Used to remove narrowed or blocked vessels. However, surgery can be costly, temporary, and may produce significant medical waste. Patients are also at risk of complications, such as blood clots and amputations.
Despite the use of advanced endoscopes, many microvascular blockages remain untreatable. These limitations highlight the urgent need for innovative solutions.
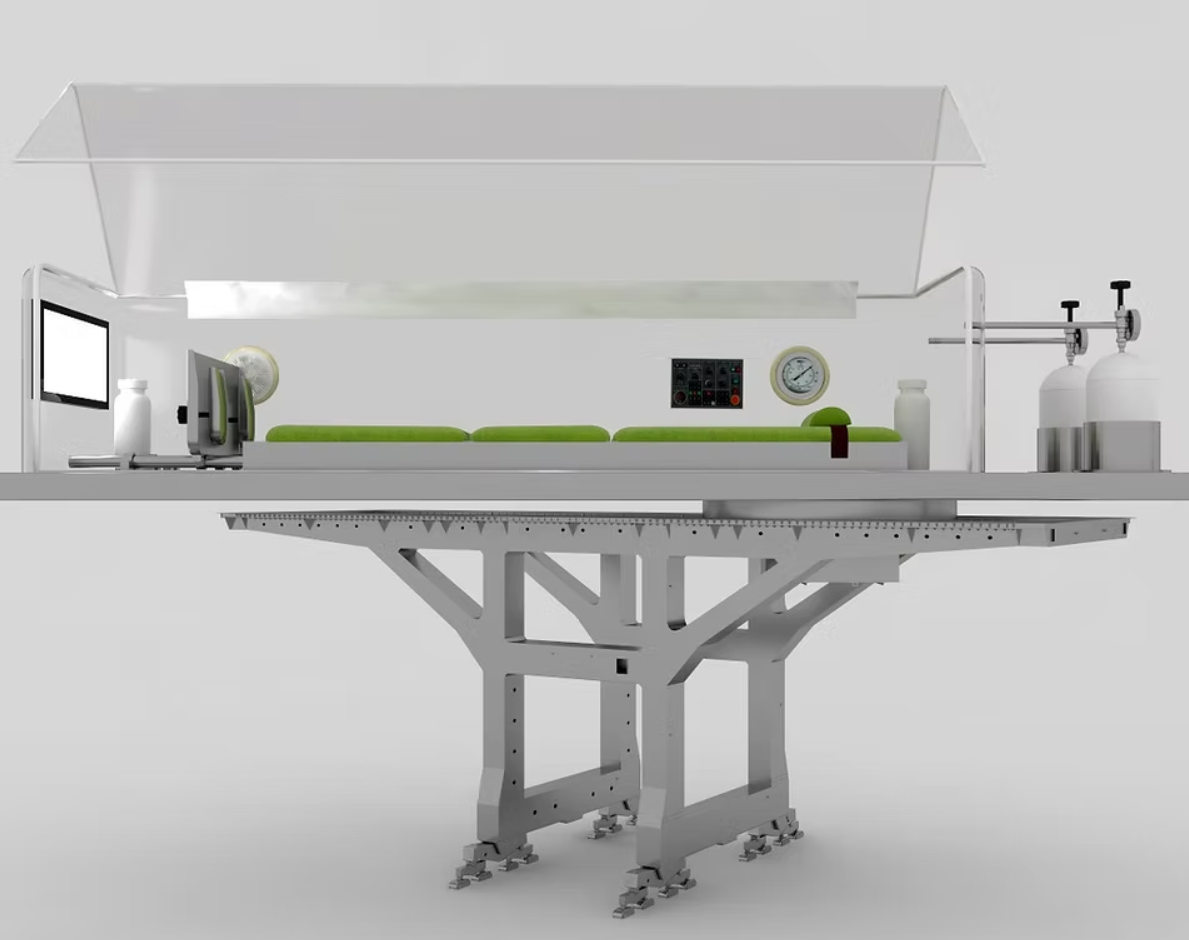
The Proposed Device
The proposed medical device, patented at the Jordanian Ministry of Industry and Trade (Patents Department), operates as an oxygen-compressed centrifuge through physiotherapy. It is designed to restore blood circulation naturally and safely, without chemical drugs or invasive surgery.
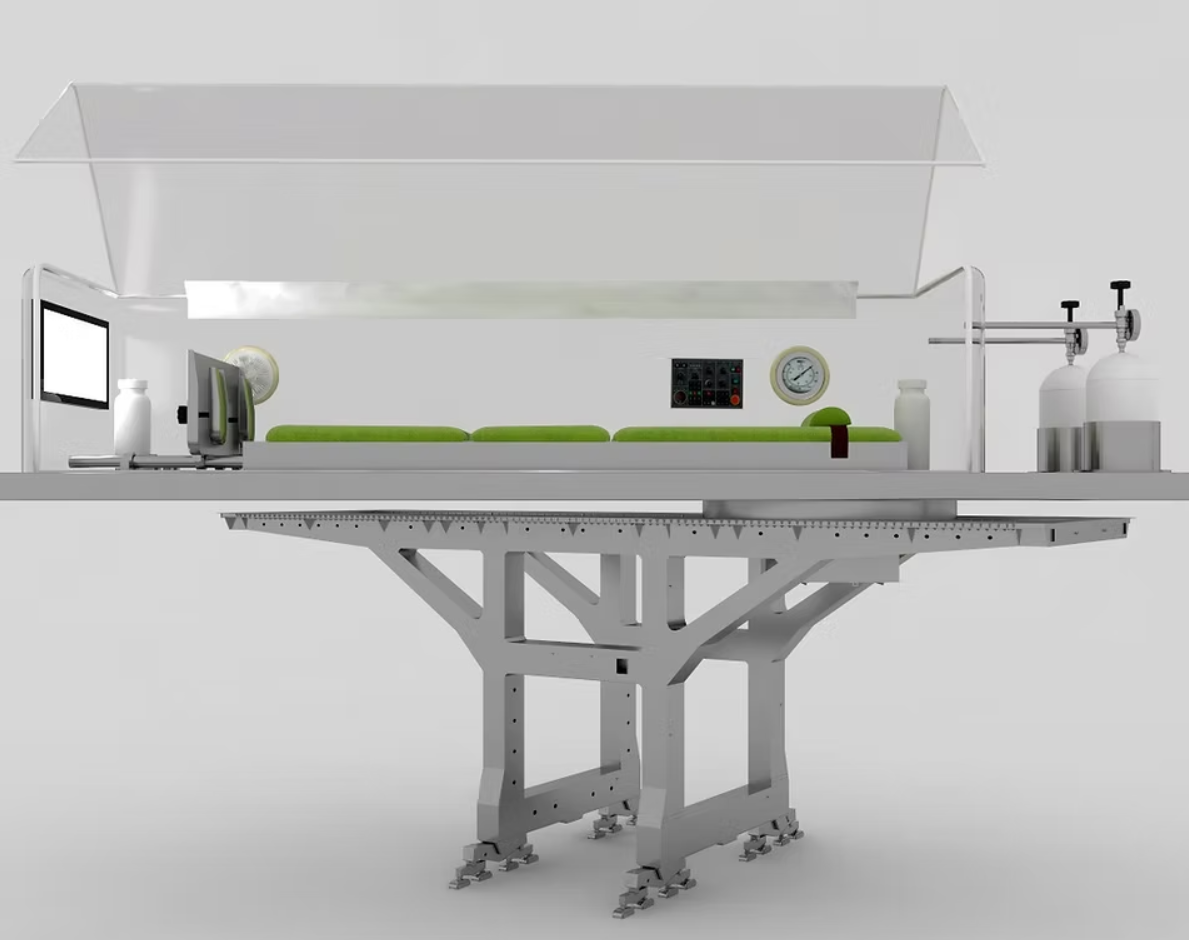

Key Features
- Non-invasive physiotherapy treatment.
- No use of chemical compounds, reducing environmental risks and medical waste.
- AI Integration: The device monitors patient vitals—including temperature, blood pressure, pulse, ECG, and oxygen levels—during treatment. AI algorithms analyze patient health status in real time, adjusting or stopping sessions as needed.
- Supervised Application: The device cannot be personally owned by patients; it must be operated in hospitals or rehabilitation centers under medical supervision.
Advantages of the Device
- Safer than surgical interventions.
- Reduces medical waste and avoids chemical pollution.
- Non-invasive and drug-free, minimizing risks to patients.
- Cost-effective: lowers healthcare expenditures and reduces reliance on incinerators for waste disposal.
- Improves patient outcomes by restoring blood circulation naturally.
Economic and Social Impact
From an economic perspective, the device could generate significant healthcare savings by limiting the need for costly surgeries and reducing medical waste management expenses. Globally, ischemia affects an estimated 30–35% of the population, equivalent to more than 400 million patients.Market projections suggest that capturing even 2% of patients in the first year—around 8 million individuals—could grow to 10% market share within seven years. Additionally, widespread adoption would create new employment opportunities for doctors, engineers, nurses, technicians, and service staff.
Patient Outcomes and Public Safety
Patients suffering from ischemia often experience severe complications, including:
- Pain and difficulty walking.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Circulatory system malfunctions.
- Organ damage (kidneys, eyes, limbs).
- In advanced cases, life-threatening infections and amputations.
Conclusion
Ischemia remains a global health challenge, closely linked to lifestyle and chronic disease risk factors. Current treatments, including drugs and surgery, are insufficient, costly, and environmentally burdensome. The proposed device offers a safer, drug-free, and non-invasive physiotherapy-based treatment alternative, enhanced with AI monitoring for personalized care. Beyond its clinical benefits, the device reduces healthcare costs, minimizes environmental risks, and presents significant economic opportunities worldwide.



